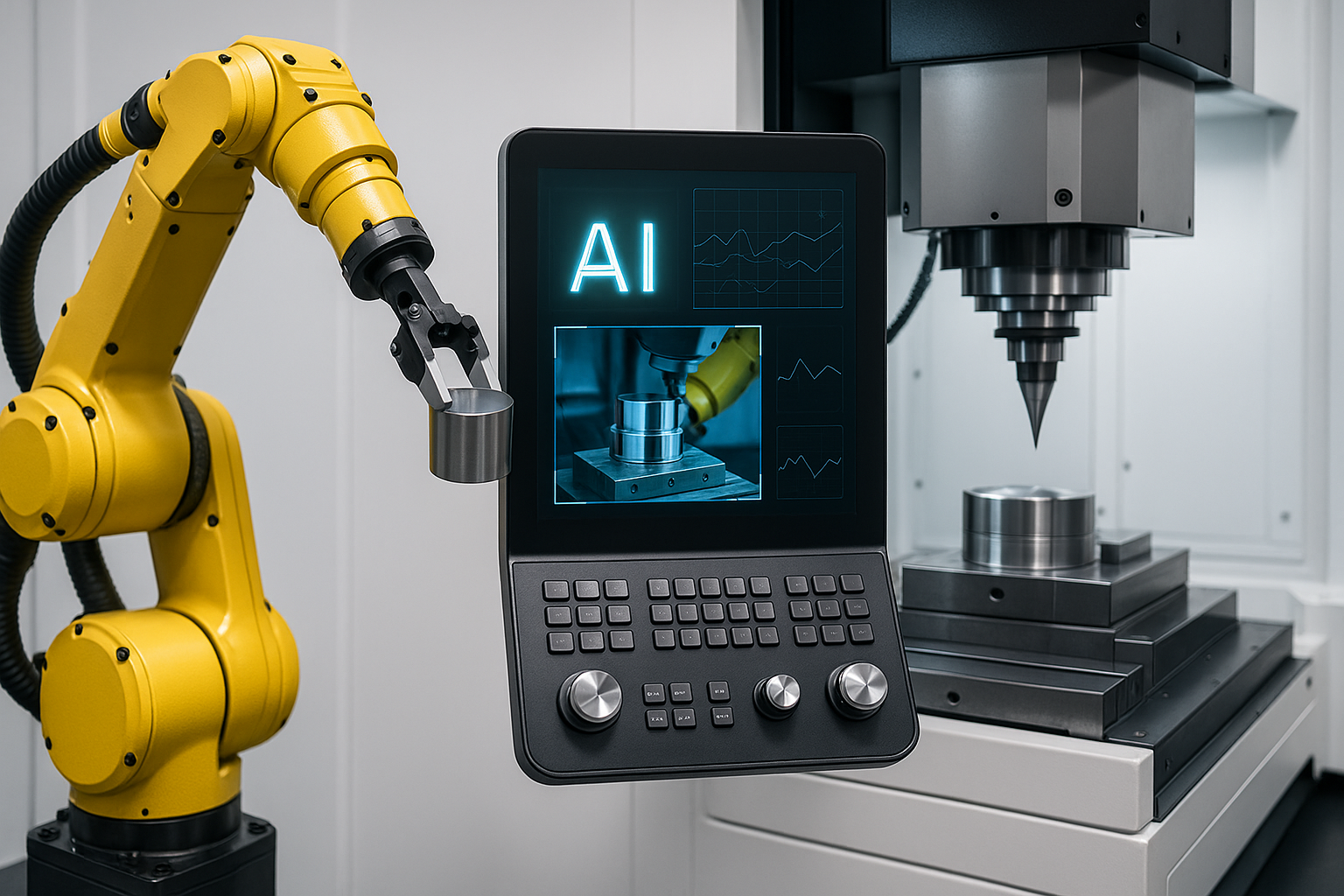
Vision assisted CNC loading cells are becoming one of the most important automation upgrades for European machine shops in 2025. These new vision assisted CNC loading cells use AI perception to locate parts, orient them correctly, and load them into the machine even when position, shape, or material condition varies. By removing the need for perfect fixturing or precise placement, vision assisted CNC loading cells finally make loading automation practical for high-mix and medium-volume machining environments.
The big shift in 2025 is not the robot itself. It is the AI-driven vision layer that handles inconsistency, detects errors in real time, and reduces stoppages caused by manual loading mistakes. This new generation of vision technology brings measurable improvements in uptime, throughput, and part quality.
Below is a breakdown of the strongest improvements, real-world performance gains, and what shops should prepare for as vision assisted CNC loading cells become mainstream across Europe.
Why Vision-Assisted CNC Loading Works Better Than Traditional Automation
Traditional loading cells require extremely rigid processes. Operators must place parts in exact positions, use dedicated trays, and maintain clear tolerances on incoming material. This works only for stable production. Reports from Engineering.com show growing adoption of AI-enabled vision systems in European machining cells.
Machine shops today deal with:
- mixed part sizes
- inconsistent part orientation
- variable batches
- scratches, burrs, and oil on surfaces
- tight deadlines
This is exactly where AI-powered vision systems excel. New robotic loading cells use:
- depth cameras
- structured lighting
- multi-angle 3D scanners
- detection models trained on thousands of part shapes
This combination gives robots the ability to handle the “unknowns” that used to stop automation completely.
For related content you can read this article too 6 Mobile Robots in Manufacturing: The Next Frontier for Metal Shops
Robots Now Recognise Parts Without Perfect Placement
Older loading systems needed precise part placement. New AI perception models detect:
- outlines
- edge profiles
- hole patterns
- milling marks
- material type
This allows the robot to pick and orient parts from random piles, bins, or conveyor surfaces.
Shops report:
- 40 to 60 percent less setup time
- fewer rejected picks
- elimination of custom trays
Faster Loading Cycles Through Adaptive Path Planning
Traditional robots ran fixed pick paths. If a part was slightly rotated, the cycle failed.
New cells perform:
- live pose estimation
- collision prediction
- speed adjustment
- clamp verification
This improves both cycle time and machine uptime. Many European users report an extra 5 to 12 percent spindle utilisation simply because the machine no longer waits for an operator to reorient the part.
Vision Systems Can Handle More Material Variations
Vision-assisted robots now recognise:
- shiny surfaces
- matte surfaces
- oiled steel
- aluminium
- forged shapes
- bar ends
- cast geometries
AI vision models adjust exposure and lighting in real time. This reduces loading failures caused by glare, coolant droplets, or inconsistent textures.
Read more about AI in CNC
Seamless Integration With CNC Controls and CAM
The newest loading cells connect directly to CNC controls and CAM software. This is the important part because robotic loading becomes part of the machining process, not an add-on.
The robot receives:
- part dimensions
- clamping rules
- orientation tolerances
- tool clearance zones
This avoids crashes and allows the robot to position parts accurately even when the part geometry changes between jobs.
What This Means for Machine Shops in 2025
More stable throughput
Operators do not need to babysit the robot or re-align parts.
Less labour pressure
Shops reduce operator time spent on low-value part loading.
More consistent feeding of the CNC machine
Spindle waits drop significantly, increasing revenue per hour.
Better fit for HMLV workflows
For the first time, robotic loading becomes practical for short runs. Vision removes the requirement for repeated custom setup.
How Vision-Assisted Loading Cells Reduce Scrap
Although loading is not traditionally seen as a scrap driver, AI loading makes several improvements:
- consistent part orientation stops misclamping
- robot checks for burrs, warping, or deformation before loading
- sensors detect if the part is the wrong type or wrong size
- vision inspection catches missing holes or edges before machining
- consistent positioning reduces rework on finishing passes
Vision systems act as a first quality gate before the machining cycle begins.
What Shops Should Prepare For Next
Machine shops adopting vision-assisted loading should plan for:
- slightly longer initial training time
- calibration routines for new materials
- collaborative zones for safe operator access
- periodic camera cleaning and alignment
- stable network infrastructure
Once deployed, these cells support unattended running for longer periods, sometimes across an entire shift. Shops adopting vision assisted CNC loading cells report better handling accuracy, especially when loading small or reflective workpieces.
Conclusion
Vision-assisted robotic loading is one of the most useful automation upgrades for CNC environments in 2025. AI-powered perception finally removes the fragile conditions older systems needed, allowing machines to run with more consistency, more autonomy, and far fewer interruptions.
As prices fall and reliability improves, vision assisted CNC loading cells are becoming one of the most practical automation upgrades for 2025. Machine shops that adopt this technology now will see clear gains in spindle utilisation, quality, and workflow reliability within the first few months. Shops investing in vision assisted CNC loading cells now are positioning themselves for the next wave of automated precision manufacturing.
MachineToolNews.ai on LinkedIn




One Comment